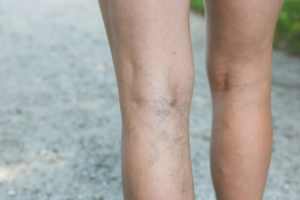
Venous illnesses arise from disorders in the veins, which interfere with the flow of blood. When a valve is dysfunctional, blood flows backward to the legs in a process known as reflux. When valves in the superficial veins are dysfunctional, they force deep veins to carry a heavier load of blood.
Venous illnesses arise from disorders in the veins, which interfere with the flow of blood. When a valve is dysfunctional, blood flows backward to the legs in a process known as reflux. When valves in the superficial veins are dysfunctional, they force deep veins to carry a heavier load of blood.
Chronic venous insufficiency occurs when deep veins clog leading to pooling of blood in the veins around the foot and leg areas. This condition is manageable with a venous stent procedure.
Diagnosis
There are various classifications of venous conditions. When blood flows to the feet and takes long to flow out, it could lead to:
· Chronic venous insufficiency
· Deep vein thrombosis
· Venous ulcer
· Varicose veins
· Skin ulcer
· Post-thrombotic syndrome
· Venous stasis
· Superficial vein thrombosis
· Stasis dermatitis
For effective diagnosis of venous conditions, you need to use innovative technology. Two tests can give you accurate results:
· Venogram test involves the use of intravenous contrast dye to color your veins opaque in the X-ray image to point out the source of the problem.
· Duplex Ultrasound involves testing the speed and direction of blood flow using a transducer device.
Treatment
Venous stent procedures have become the preferred treatment method for most venous conditions. The stent is a tubular support placed inside the affected veins to relieve obstruction.
Medical professionals advise that the stent should decompress the damaged veins to reduce congestion in the tissues. The stent establishes blood flow back to the heart. Medical experts should use only one type of stents with the right size to avoid complications.
Studies show that one in five men and one in three women above the age of 50 have venous conditions. Should you need treatment, consult healthcare providers offering the latest technology.